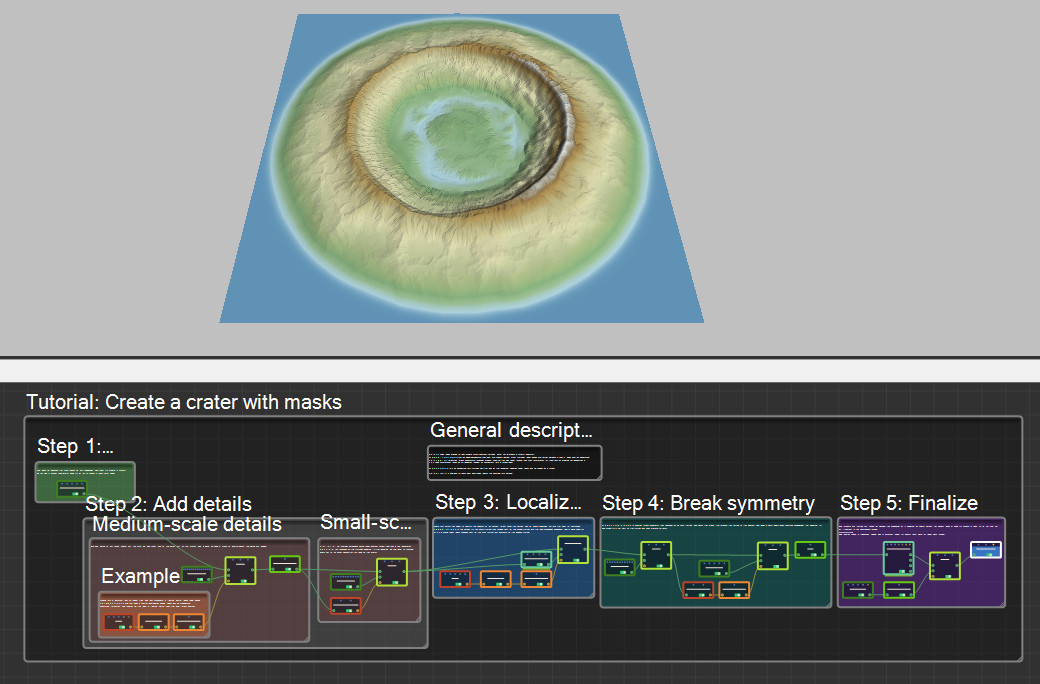
This project uses masks to help create more complex terrains. Here, we will create a crater landform.
Masks, represented by yellow connectors and links, are objects distinct from terrains. Their values are limited between 0 and 1. They can be generated, painted, or imported. Mask generators produce masks, such as the Disk node, without any prior information, or they can be created by converting a terrain's information, such as its elevation, slopes, or curvature, into a mask layer.
Masks can also be converted into terrains with the help of the Constant Elevation node, which can be guided by a mask.
Select Help > Samples to access the sample project.
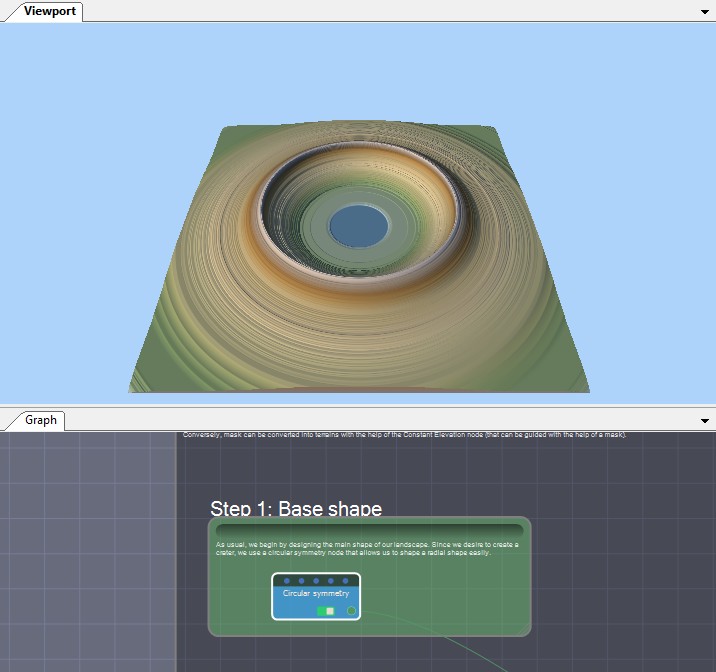
Step 1: Base shape
We begin by designing the main shape of our landscape. We want to create a crater, so we use a Circular symmetry node to let us to shape a radial form easily.
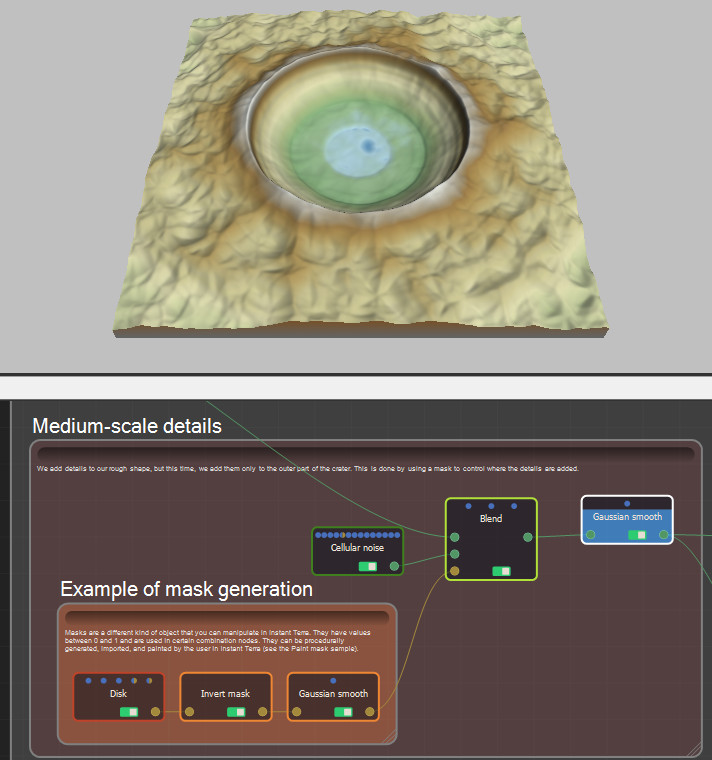
Step 2: Add details
Medium-scale details: We add details to our rough shape, but this time, we add them only to the outer part of the crater. This is done by using a mask to control where the details are added. Masks are a different kind of object that you can manipulate in Instant Terra. They have values between 0 and 1 and are used in certain combination nodes. They can be procedurally generated, imported, and painted by the user in Instant Terra (see the Paint mask project).
Small-scale details: Similarly, we remove small-scale details using another mask. This one is not generated ex-nihilo, but depends on the terrain's elevation. In this example, we only want to remove some dirt at an upper location on the ridge of the crater.

Step 3: Localized erosion
There are often two ways to control the location of an effect: either apply the effect only at some locations, like with the Add or Subtract nodes, or apply the effect to the entire terrain and replace part of the original terrain with the new processed landscape. This is done using an Alpha blend node, which replaces part of the first terrain with elements of the second terrain.

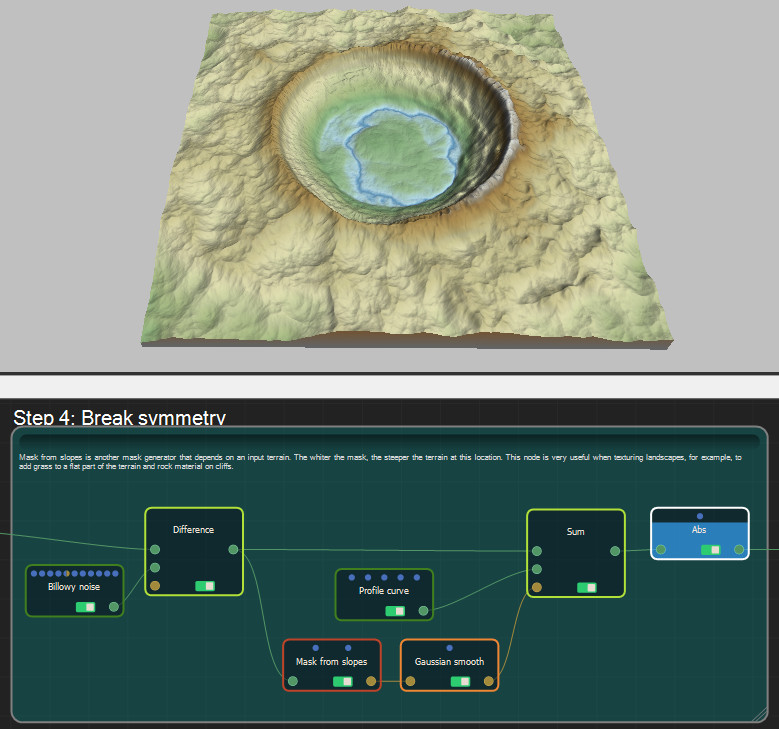
Step 4: Break symmetry
Mask from slopes is another mask generator that depends on an input terrain. The whiter the mask, the steeper the terrain at this location. This node is very useful when texturing landscapes, for example, to add grass to a flat part of the terrain and rock material on cliffs.
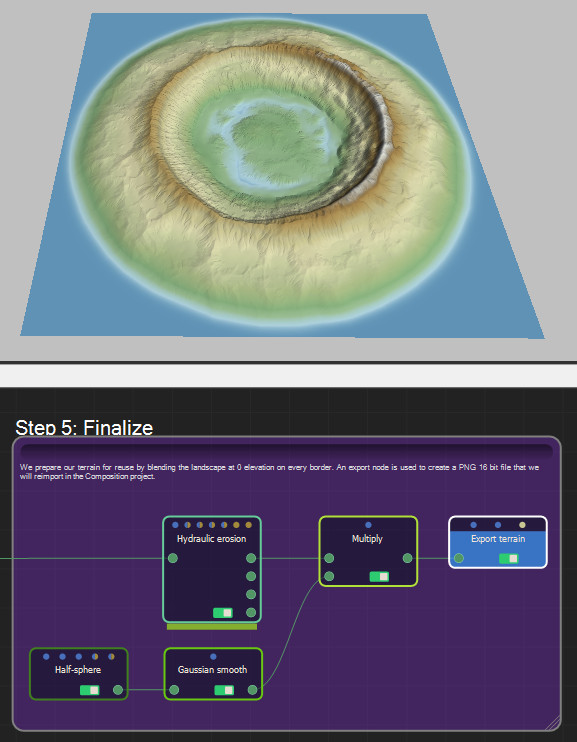
Step 5: Finalize
We prepare our terrain for reuse by blending the landscape at 0 elevation on every border. An export node is used to create a PNG 16 bit file that we will reimport in the Composition project.