Adding a Stamping node
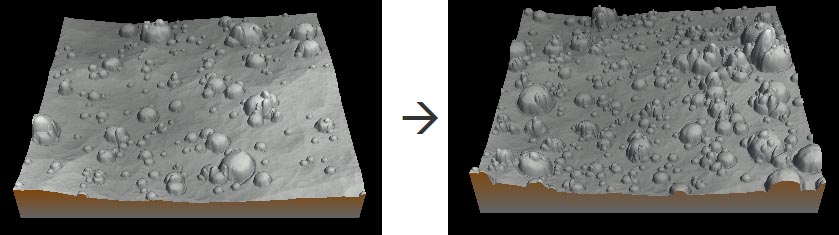
The Stamping node inserts copies of a terrain on a second terrain. The node has two inputs: the base terrain is linked to the top connector and the terrain to use as the stamp to the second connector.
An optional mask connector allows a density mask to be used in the stamp. This option constrains the stamping to a part of the terrain. This may not be respected if the number of stamps is too high.

To add a Stamping node, right-click in the Graph Editor and select Create Node > Terrain Composition > Stamping.
Select the node to open its parameters:
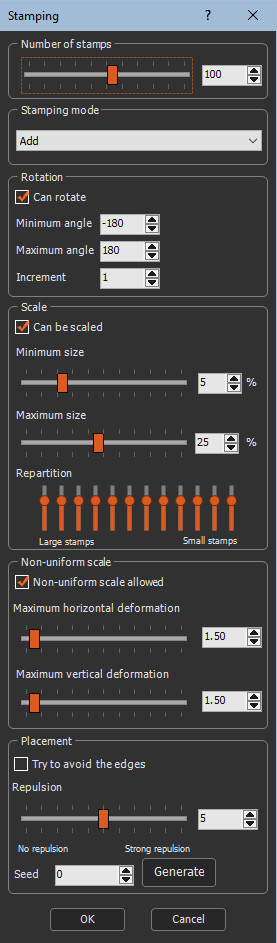
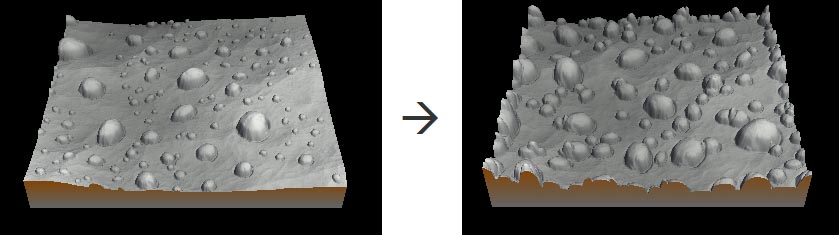
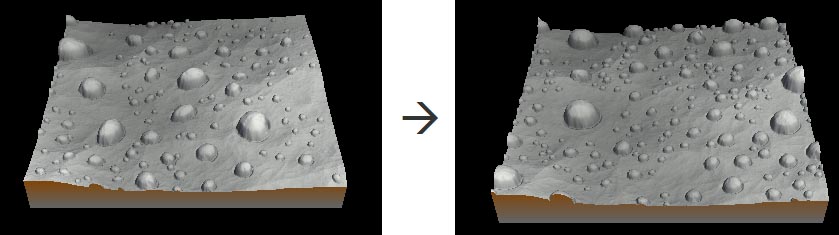
Setting the number of stamps
This parameter defines the number of stamps in the terrain.
A larger value adds more stamps.
A smaller value adds less stamps.

Setting the stamping mode
This parameter defines the how the stamp is placed in the terrain.
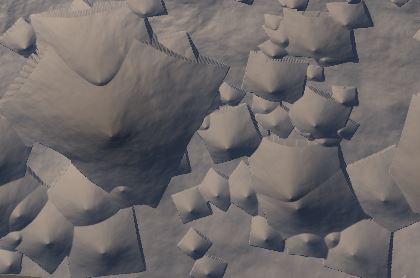
- Add: Adds the stamp to the terrain to create a raised landscape. When stamps are overlapping, their elevations are added.

- Max: Adds the stamp to the terrain to create a raised landscape. When several stamps are at the same location, the maximum elevation of these stamps is used at each vertex.

- Subtract: Subtracts the stamp from the terrain. For instance if the elevation of the stamp is between 0 and +10, the result is a hole whose depth will be between 0 and 10 meters. The stamp is inverted (positive elevations become negative elevations) and then added.

- Min: Similar to Subtract, but when several stamps are at the same location, the minimum elevation of these stamps is used at each vertex.
Setting the rotation
These parameters control the way the stamp can rotate. The default values let a complete 360° freedom of rotation, with a pace of 1°.
- Can rotate: When checked, the stamp can be rotated.
- Minimum angle: Sets the minimum rotation angle allowed down to -180°.
- Maximum angle: Sets the maximum rotation angle allowed up to 180°.
- Increment: Sets the minimum pace of
rotation.
For example if you set 90°, only 4 positions will be possible: - Initial position
- +90°
- -90°
- 180°

Setting the scaling
This parameter sets the percentage of scaling of the stamp and the repartition of the different sizes of stamps.
- Can be scaled: When checked, the stamp can be scaled.
- Minimum size: Sets the minimum allowed scale as a percentage of the stamp.
- Maximum size: Sets the maximum allowed scale as a percentage of the stamp.
- Repartition: Sets the distribution of large and small stamps using 10 vertical sliders corresponding to the different stamp sizes.
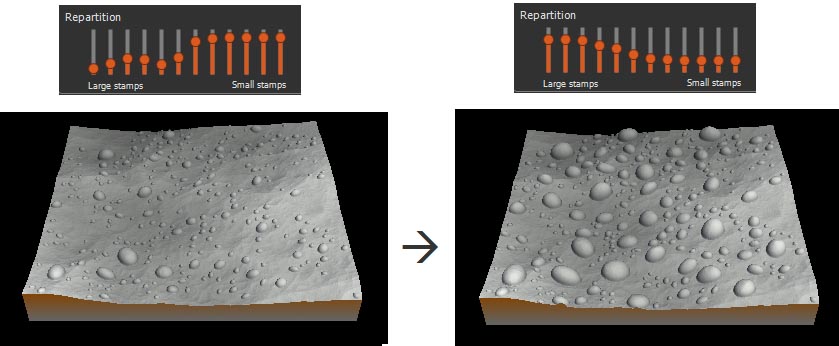
To set the repartition to the default values, right-click and select Reset.
Setting the non-uniform scaling
This parameter sets the non-uniform scaling along the horizontal and vertical axes.
- Non-uniform scale allowed: When checked, the stamp can be scaled non-uniformly.
- Maximum horizontal deformation: Sets the maximum horizontal deformation on a scale of 1 (no deformation) to 10 (10 times longer than large)..
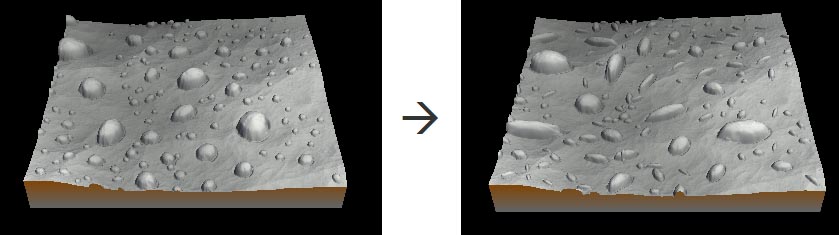
- Maximum vertical deformation: Sets the maximum vertical deformation on a scale of 1 (no deformation) to 10 (10 times the initial elevation of the stamp).

Setting the placement
This parameter sets the distribution of the stamp.
Instant Terra tries to respect the density input mask as much as possible, but if the number of stamps is too high, there will be cases where the position of the stamps will not respect the density mask. In this case, the number of stamps or the repulsion must be reduced.
- Try to avoid the edges: When checked, the stamp is not constrained within the terrain. The stamp can be placed on the terrain border.

- Repulsion: Intensity of the repulsion force between each stamp, from 0 (stamps can overlap) to 10 (maximum repulsion between each stamp). In case of too numerous stamps, this may not be respected.
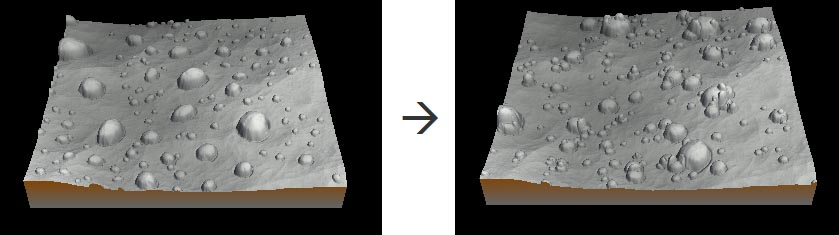
- Seed: Value of the noise generation seed. Changing the value of the seed (even very slightly) completely changes the terrain's appearance. Press Generate to vary the seed.
Parameters
| Parameter | Use | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of stamps | Defines the number of stamps in the terrain.. | |
| Stamping mode | Defines the how the stamp is placed in the terrain. | |
| Add | Adds the stamp to the terrain to create a raised landscape. | |
| Subtract | Subtracts the stamp from the terrain. | |
| Min | Similar to Subtract, but when several stamps are at the same location, the minimum elevation of these stamps is used at each vertex. | |
| Max | Adds the stamp to the terrain to create a raised landscape. When several stamps are at the same location, the maximum elevation of these stamps is used at each vertex. | |
| Rotation | Sets the angle of rotation of the stamp. | |
| Can rotate | When checked, the stamp can be rotated. | |
| Minimum angle | Sets the minimum rotation angle down to -180°. | |
| Maximum angle | Sets the maximum rotation angle up to 180°. | |
| Increment | Sets the minimum angle of rotation. | |
| Scale | Sets the percentage of scaling of the stamp and the repartition of the different sizes of stamps. | |
| Can be scaled | When checked, the stamp can be scaled. | |
| Minimum size | Sets the minimum scale as a percentage of the stamp. | |
| Maximum size | Sets the maximum scale as a percentage of the stamp. | |
| Repartition | Sets the distribution of large and small stamps using 10 vertical sliders corresponding to the different stamp sizes. | |
| Non-uniform scale | Sets the non-uniform scaling along the horizontal and vertical axes. | |
| Non-uniform scale allowed | When checked, the stamp can be scaled non-uniformly. | |
| Maximum horizontal deformation | Sets the maximum horizontal deformation on a scale of 0 to 10. | |
| Maximum vertical deformation | Sets the maximum vertical deformation on a scale of 0 to 10. | |
| Placement | Sets the distribution of the stamp. | |
| Try to avoid the edges | When checked, the stamp is constrained within the terrain. This may not be respected if the repulsion intensity is too high.. | |
| Repulsion | Intensity of the repulsion force between each stamp, from 0 (stamps can overlap) to 10 (maximum repulsion between each stamp)..This may not be respected if the number of stamps is too high. | |
| Seed | Value of the noise generation seed. |